Addictive Content
How to Block Porn on a Home Router
Learn how to install a content filter to block adult content on your home internet and Wifi.
Network filtering allows you to block content on any device (smartphones, tablets, computers, TVs) that uses your home internet connection.
I've written this guide after several years of testing the best methods for blocking unwanted content on many different devices.
Network content filtering is a critical part of my recommended approach to setting up an effective porn-blocking system .
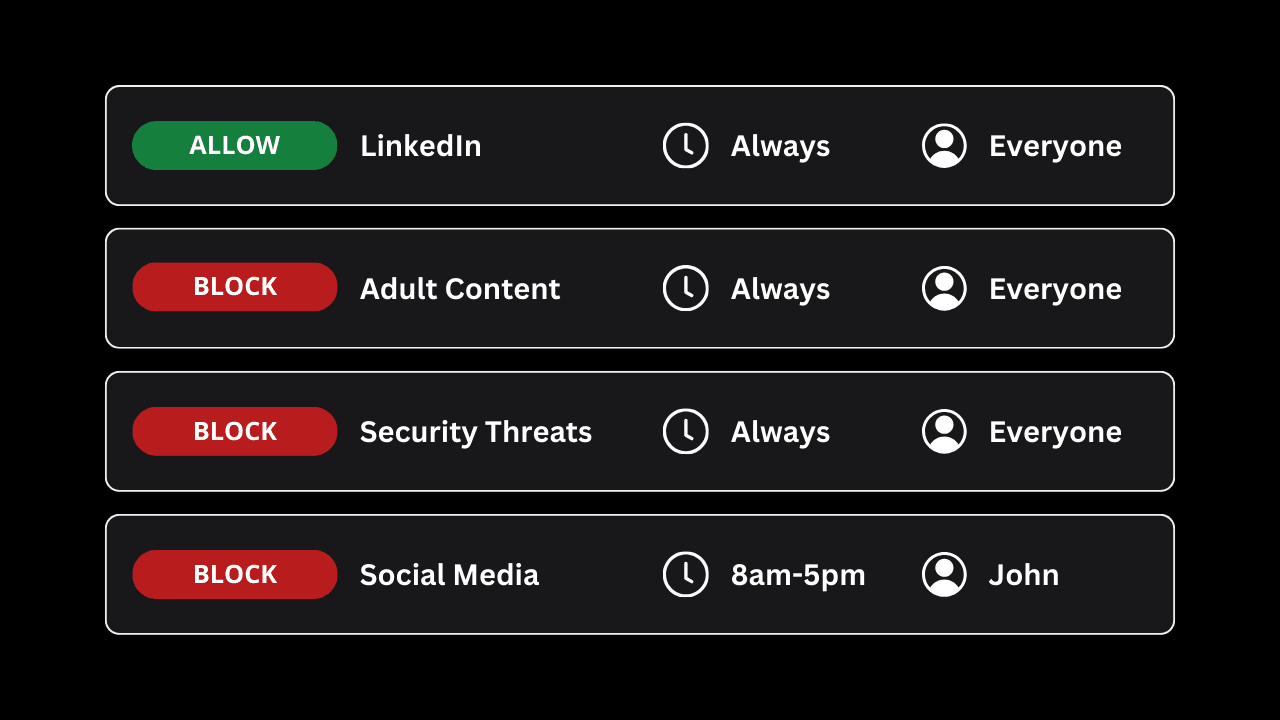
This guide assumes that you will use a filtering service, like the one provided by Tech Lockdown, that allows you to customize the filtering settings.
I only recommend using a customizable filter because it's important that you are able to select the categories you want to block and also add additional websites to an allow/block list.
How to Login to your Router
You must login to your router to complete this guide.
Find IP Address Type
If you are setting up a DNS Filtering service on your home network to block unwanted content, your IP address type will determine how you connect to that service. In some cases, your IP address type may not be supported by the filter you are using.
There are currently two types of IP addresses:
- IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numbers, written as four decimal numbers separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
- IPv6 addresses, on the other hand, are written as eight groups of hexadecimal numbers separated by colons (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
You can use this IP address testing tool to check if IPv6 is enabled on your network.
If the test shows that no IPv6 address is detected, then you must follow the IPv4 setup guide or enable IPv6 on your home network.
How to Enable IPv6
If you want to use a filtering service that supports IPv6, enabling IPv6 can simplify the setup process. Some internet connections support IPv6, but it's not enabled on the router by default.
- Enable IPv6: Look for a toggle switch or checkbox labeled "IPv6" or "IPv6 Enabled" and turn it on. Some routers may require you to choose a specific IPv6 mode, such as "Native" or "Tunnel". Consult your router's manual or online documentation for more information on the specific modes available.
After IPv6 is confirmed, ensure that IPv4 is now disabled on your router.
A) IPv4 Setup Instructions
Just like you have a home address that represents where you physically live, an IPv4 address represents the address of your home internet connection.
Connecting a home network with an IPv4 address to a filtering service depends on two steps:
- You must add your home network address to the filtering service
- You must point your router to the filtering service
Find Address Type
There are currently two types of IP addresses:
- IPv4 addresses are 32-bit numbers, written as four decimal numbers separated by periods (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
- IPv6 addresses, on the other hand, are written as eight groups of hexadecimal numbers separated by colons (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
You can use this IP address testing tool to check if IPv6 is enabled on your network.
If the test shows that no IPv6 address is detected, then you must follow the IPv4 setup guide or enable IPv6 on your home network.
Dynamic IPv4 Address
A dynamic IPv4 address can sometimes change, especially if you lose power and your internet connection resets. This often results in a completely new IPv4 address.
When an IPv4 address changes, it's similar to you moving into a different house. If you move to a different house you always change your shipping address on all of the services you use.
You need to do the same thing when your IPv4 address changes.
If your IPv4 address changes and the filtering service is using your old IP address, your filter and potentially your entire internet connection will stop working because the service won't be able to find your home network.
There are two strategies for automatically handling IPv4 address changes:
- Use an IP updater application
- Use a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) service
The best way to automatically handle IP changes is by using a Dynamic DNS (DDNS) service. Instead of using an IP address to represent your home network, like 123.45.67.89, we will configure a hostname like myhomenetwork.ddns.net.
Using an IP updater VS DDNS
Some filtering services don't support dynamic DNS via hostnames. Instead, they provide an IP updater application that you install on a computer that is usually connected to your home network.
It might seem simpler to set up an application, like the one provided by OpenDNS, to automatically handle IP address updates.
I do not recommend using an IP updater.
The issue with this approach is that the updater client has to be running on a computer that is constantly connected to the home network. If you turn off the computer and your internet connection resets, the IP change won't be sent to the filter. As a result, filtering (and possibly your entire internet connection) will stop working.
Additionally, if you install a VPN on the computer that runs the IP updater application, it will send the wrong IP address to the filter service and break filtering for the entire network.
Furthermore, it's easy to circumvent filtering with this approach by uninstalling the IP updater application and restarting the router. This would change the IP address of the home network, but without updating the filter with the new IP.
Using a DDNS service is one of the best methods for handling IP address changes.
Check Filter Support for Dynamic DNS
Before setting up a dynamic DNS service, verify that the filtering service you use supports using a hostname.
However, if you're using a service like OpenDNS Home , hostnames aren't supported.

Configure DDNS service
Centurylink router example:
Xfinity router example:
Most routers allow you to select NoIP as the service provider. If not, you'll manually configure. Choose the option supported by your router:
Test NoIP to make sure that when your IPv4 address changes NoIP detects the change.
Alternatively, you can use a computer to quickly check what IP address is associated with your NoIP hostname by doing the following:
You'll see the IP address associated with your NoIP hostname.
Update filter to use DDNS hostname
Once you confirm that the DDNS service works properly, you can update your filtering account to use a hostname instead of an IP address.
Static IPv4 Address
Most Internet Service Providers (ISPs) automatically assign a Dynamic IP address to your router, which means your router's IP address could change if the power goes out, for example. However, some ISPs also allow you to specify a Static IP address to your that does not change
You might want to change to a Static IP address if your router does not support DDNS.
Change Router DNS
Once you've added your public network address to the filter you are using, you need to update your router to point to the filter.
B) IPV6 Setup Instructions
One of the benefits of a home network with IPv6 addresses is that pointing your router to your desired filter is a relatively straightforward process.
Your filtering service will provide you with DNS server addresses that are unique to your filter account.
In your router, simply update the primary and secondary DNS server addresses to point to the addresses provided by your filter:
Troubleshooting
DNS filters can be frustrating to maintain and configure. They can break for various reasons, but in my years running my own DNS Filtering service, here are the common reasons:
Something Broke. How do I get my internet back?
If something is misconfigured and you can't browse the internet or you're having some other issue, you can revert your configuration back to it's initial state.
Change your DNS servers to be automatically generated instead of manually set to your filter's IP addresses.
You can login to your router without internet by entering one of these addresses in your browser (only one address will work, so try both):
192.168.0.1 192.168.1.1
I set everything up, but filtering isn't working
Double check that you followed all of the required steps and that you are pointing your router's primary and secondary DNS to your filter.
Disable router parental control features
The most common conflict is parental control features on the router. Disable any parental control features and check for any privacy or filtering features that might be enabled.
Caching
Another common reason is the DNS and browser cache. Sometimes a device will save a page or website that you have visited previously.
Here are some methods you can try:
- If you are on a computer, try flushing your DNS cache (see above instructions).
- Restart your browser and open an incognito/private browsing window, then visit a website that should be blocked (you should use a test website provided by your filter).
- Restart your device
- Wait 10-15 minutes
- Restart your router (unplug it and plug it back in)
Validate DNS with DNSLeaktest
If content still isn't being filtered, go to dnsleaktest.com website and run an extended test.
When the test finishes, the ISP column should correspond to the filter service you are using. If, for example, your ISP (internet service provider) is Verizon, you should not see Verizon in the ISP or hostname column. This is because you are no longer pointing directly to your ISP. You're first pointing to the filter, which then routes to your ISP.
VPNs and Proxies
Validate that your computer or smartphone is not using a VPN or proxy. You can also use DNS Leaktest to check this.
Check your device
Overriding DNS
Your device might be setting its own primary and secondary DNS servers instead of obtaining them automatically.
For example, in Windows network settings, you should see that the DNS server assignment is automatic
If it's manually set, edit it so that it's automatically assigned.
IP Changes
One of the biggest reasons that filtering services stop working is due to IPv4 address changes. Most home networks have a dynamic public IP address. This means that the address can change, especially if your internet connection resets for some reason.
If your IP address changes and the filtering service is still referencing the old IP address, content filtering will completely stop working. In some cases, your internet might break, which makes it difficult to login to the filtering service to update the IP address.
You configure the filtering service to use a hostname instead of an IP address . This automatically handles any address changes for you so that your setup works long-term.
My Internet is not working (IPv4 with Dynamic DNS)
Internet not working? double check the following:
Expired NoIP Hostname
A common reason why filtering or internet worked previously, then it suddenly stops working, is due to an expired NoIP hostname.
Recall that NoIP hostnames expire every 30 days with a free plan. If you didn't renew the hostname, it might have expired.
If you have NoIP, sign in to your account and make sure that your hostname has the "active" tag. If it doesn't then you need to renew it.
NoIP hostname IP address is wrong
It's possible that your router didn't properly send IP changes to NoIP, so NoIP might have an incorrect IP address representing your home network.
If this resolves your issue, you now need to figure out why your NoIP hostname did not automatically update with your changed IP address. You should repeat the IPv4 guide starting after you create your NoIP account.
Intentional network setting changes
Another common issue has to do with a user configuring network settings that allow them to bypass filtering entirely. Some DNS Filters, such as the one I provide, include an application that can force specific network settings. Even if a user attempts to use an alternative DNS, the application will revert the changes.
Furthermore, you can also block personal VPNs and proxies (not a VPN provided by your job), which are no longer necessary if you use a DNS filtering service (they have the same privacy affect).
A modern DNS Filtering service should automatically block most VPNs and proxies, but you can go a step further and configure managed devices that restrict the ability to set a VPN from the device itself.